▶ 초음파 센서 이론적 배경
1) 초음파센서 핀 안내

2) 초음파 센서 동작원리

▶ [실습 1] 초음파 센서로 거리측정하기(시리얼 모니터로 거리확인)
- 회로 구성

- 핀연결
VCC - > 5V
GND - > GND
TRIG -> PIN 9
ECHO -> PIN 8
- 코드 복사 붙여 넣기.
#define TRIG 9 //TRIG 핀 설정 (초음파 보내는 핀)
#define ECHO 8 //ECHO 핀 설정 (초음파 받는 핀)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //PC모니터로 센서값을 확인하기위해서 시리얼 통신을 정의해줍니다.
//시리얼 통신을 이용해 PC모니터로 데이터 값을 확인하는 부분은 자주사용되기 때문에
//필수로 습득해야하는 교육코스 입니다.
pinMode(TRIG, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ECHO, INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
long duration, distance;
digitalWrite(TRIG, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TRIG, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TRIG, LOW);
duration = pulseIn (ECHO, HIGH); //물체에 반사되어돌아온 초음파의 시간을 변수에 저장합니다.
//34000*초음파가 물체로 부터 반사되어 돌아오는시간 /1000000 / 2(왕복값이아니라 편도값이기때문에 나누기2를 해줍니다.)
//초음파센서의 거리값이 위 계산값과 동일하게 Cm로 환산되는 계산공식 입니다. 수식이 간단해지도록 적용했습니다.
distance = duration * 17 / 1000;
//PC모니터로 초음파 거리값을 확인 하는 코드 입니다.
Serial.println(duration ); //초음파가 반사되어 돌아오는 시간을 보여줍니다.
Serial.print("\nDIstance : ");
Serial.print(distance); //측정된 물체로부터 거리값(cm값)을 보여줍니다.
Serial.println(" Cm");
delay(1000); //1초마다 측정값을 보여줍니다.
}
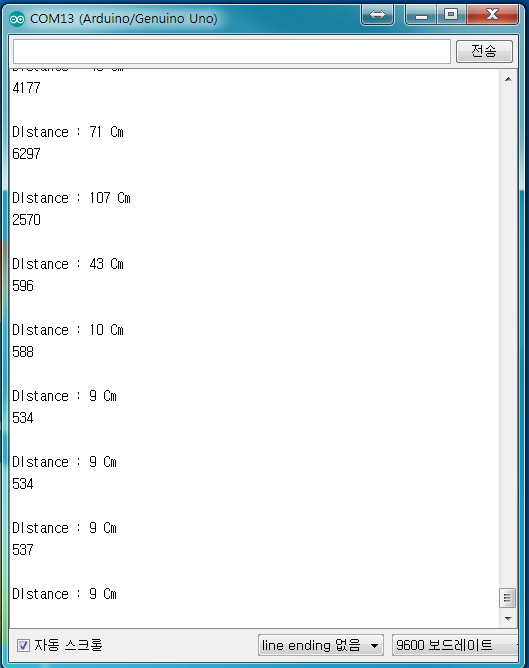
- 결과 확인

- 거리 측정

- 거리 확인
▶ [실습 2] Processing을 활용하는 아두이노 비주얼 라이징
- 동작 안내 영상
- Processing 설치
-> 구글에서 Processing 검색 후 다운로드

- 회로 구성

- 하드웨어 예시
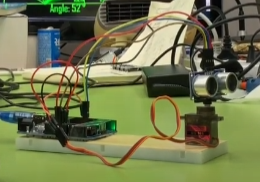
[도전 과제]
★ 챌린징 포인트 ★
- 2개의 제시되는 코드(서보모터 양방향 회전 코드 + 초음파 센싱 코드)를 하나의 동작 코드로 합쳐
1. 서보모터 양방향 회전 코드
#include<Servo.h> //Servo 라이브러리를 추가
Servo servo; //Servo 클래스로 servo객체 생성
int value = 0; // 각도를 조절할 변수 value
int ii = 0; // for 구문의 변수 선언
void setup() {
servo.attach(7); //맴버함수인 attach : 핀 설정
}
void loop() {
for(ii = 0; ii < 180 ; ii++)
{
servo.write(ii);
delay(30);
}
for(ii = 179; ii > 0; ii--) // ii-- : ii가 1씩 작아진다.
{
servo.write(ii);
delay(30);
}
}
2. 초음파 센싱 코드
// Includes the Servo library
#include <Servo.h>.
// Defines Tirg and Echo pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor
const int trigPin = 10;
const int echoPin = 11;
// Variables for the duration and the distance
long duration;
int distance;
// 힌트 : 서보모터 객체 생성 해 주세요~!
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an Output
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an Input
Serial.begin(9600);
// 힌트 : 서보모터 핀연결 세팅
}
void loop() {
// 서보모터가 반시계 방향으로 돌아갈때 코드
distance = calculateDistance();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree
Serial.print(i); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port
Serial.print(","); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port
Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
// 서보모터가 시계 방향으로 돌아갈때 코드
distance = calculateDistance();
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.print(".");
}
// 초음파 센서 거리 계산 함수 선언
int calculateDistance(){
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
// Sets the trigPin on HIGH state for 10 micro seconds
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
distance= duration*0.034/2;
return distance;
}
- 코드 완성 후
서보모터가 양방향으로 움직이면서 센싱이 잘 되는지 시리얼 모니터로 확인!!
- 프로세싱 전에 아두이노에 아래 코드 올려주세요.
- 트리거, 에코핀, 서보모터 핀 하드웨어 꼭 맞춰주기.
// Includes the Servo library
#include <Servo.h>.
// Defines Tirg and Echo pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor
const int trigPin = 10;
const int echoPin = 11;
// Variables for the duration and the distance
long duration;
int distance;
Servo myServo; // Creates a servo object for controlling the servo motor
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an Output
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an Input
Serial.begin(9600);
myServo.attach(
); // Defines on which pin is the servo motor attached
}
void loop() {
// rotates the servo motor from 15 to 165 degrees
for(int i=15;i<=165;i++){
myServo.write(i);
delay(30);
distance = calculateDistance();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree
Serial.print(i); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port
Serial.print(","); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port
Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing
}
// Repeats the previous lines from 165 to 15 degrees
for(int i=165;i>15;i--){
myServo.write(i);
delay(30);
distance = calculateDistance();
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.print(".");
}
}
// Function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor
int calculateDistance(){
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
// Sets the trigPin on HIGH state for 10 micro seconds
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
distance= duration*0.034/2;
return distance;
}
- 프로세싱 코드 업로드
myPort = new Serial(this,"COM3", 9600); // starts the serial communication
이부분에서 아두이노 연결된 COM의 숫자 확인 하고 맞추어 주기.
import processing.serial.*;
Serial myPort;
String myString = null;
int angle = 0;
int distance = 0;
void setup(){
size(1200, 700);
background(0);
myPort = new Serial(this, "COM3", 9600);
}
void draw(){
noStroke();
fill(0,7);
rect(0,0,width,height);
drawRader();
drawLine();
drawObject();
}
void serialEvent(Serial p){
try{
myString = p.readStringUntil('.');
String[] list = split(myString, ',');
angle = int(list[0]);
distance = int(list[1].replace(".",""));
}catch(Exception e){
print(e);
}
}
void drawRader(){
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2, height);
noFill();
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(98, 245, 31);
// draw the arc lines
arc(0, 0, width, width, PI, TWO_PI);
arc(0, 0, width*2/3, width*2/3, PI, TWO_PI);
arc(0, 0, width*1/3, width*1/3, PI, TWO_PI);
// draw the angle lines
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(30)), -width/2*sin(radians(30)));
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(60)), -width/2*sin(radians(60)));
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(90)), -width/2*sin(radians(90)));
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(120)), -width/2*sin(radians(120)));
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(150)), -width/2*sin(radians(150)));
// draw text
textSize(15);
fill(98, 245, 31);
textAlign(RIGHT);
text("10cm", width*1/6, 0);
text("20cm", width*2/6, 0);
text("30cm", width*3/6, 0);
popMatrix();
}
void drawLine(){
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2, height);
strokeWeight(4);
stroke(98, 245, 31);
line(0, 0, width/2*cos(radians(angle)), -width/2*sin(radians(angle)));
popMatrix();
}
void drawObject(){
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2, height);
strokeWeight(4);
stroke(255, 10, 10); // red color
float d = (width/2.0/30.0)*(float)distance;
if( d < width/2)
line(d*cos(radians(angle)), -d*sin(radians(angle)), width/2*cos(radians(angle)), -width/2*sin(radians(angle)));
popMatrix();
}
- 동작 확인

'메이커 프로젝트 > 아두이노 +' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 아두이노 DC 모터 제어하기 (0) | 2021.09.03 |
|---|---|
| [모듈 1-6] 아두이노 부저로 소리내기(feat. 전자 피아노 만들기) (2) | 2020.09.22 |
| [모듈 1-4] 아두이노 시리얼통신 제어(Feat. 로봇팔 만들기) (3) | 2020.09.08 |
| [모듈 1-3] 아두이노 서보모터 제어하기 (feat. For 구문) (19) | 2020.09.06 |
| [모듈 1-2] 아두이노 스위치 제어(feat. if-else 구문) (10) | 2020.09.06 |



